Types of metal working processes
Metalworking processes are a series of processing methods used to change the shape, size or properties of metal materials. These processes can be roughly divided into cold forming, hot forming, casting, forging, welding and cutting processing and other categories.
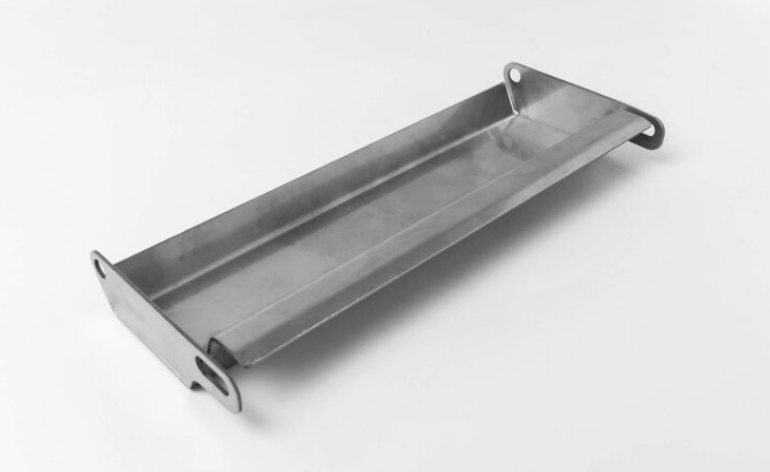
1.Cold forming
Carried out at room temperature, without changing the crystal structure of the metal, common cold forming processes include bending, stamping, shearing, etc.

2.Hot forming
By heating the metal becomes soft, easy to plastic deformation, including hot bending, hot stamping and so on.

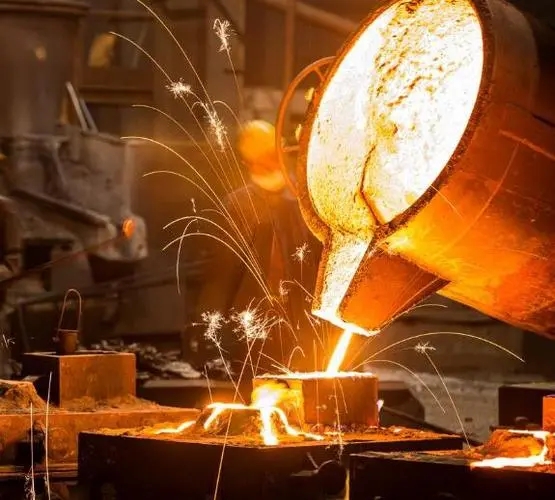
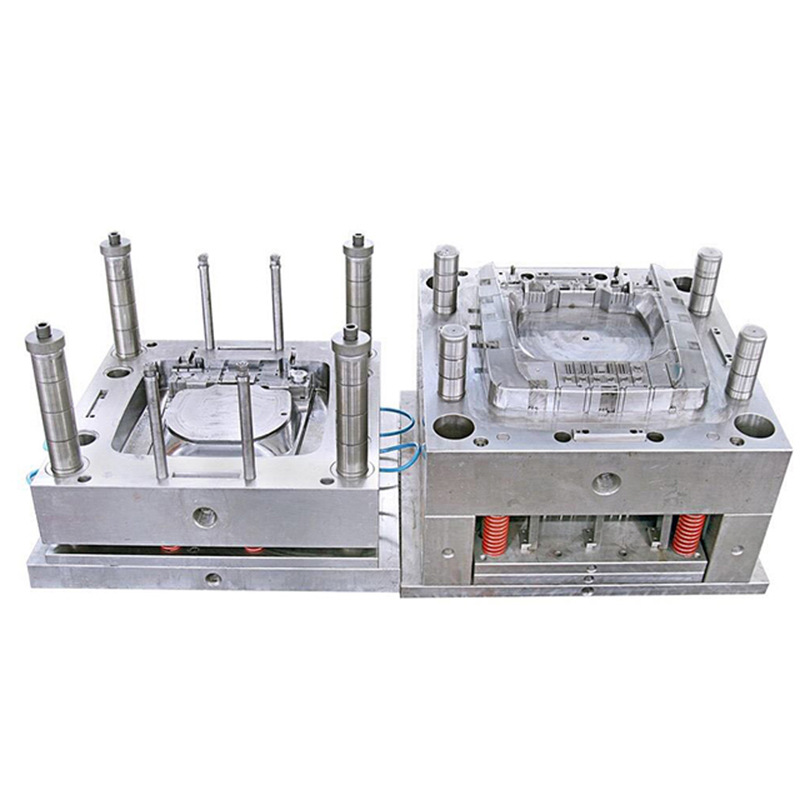
3.Casting
Molten metal is poured into the mold and cooled to form, which can produce parts with complex shapes or delicate internal structures, suitable for single piece production and mass production. It has a wide range of material sources and low cost, but the defects and internal stresses that may occur during the casting process will affect the quality of the product.
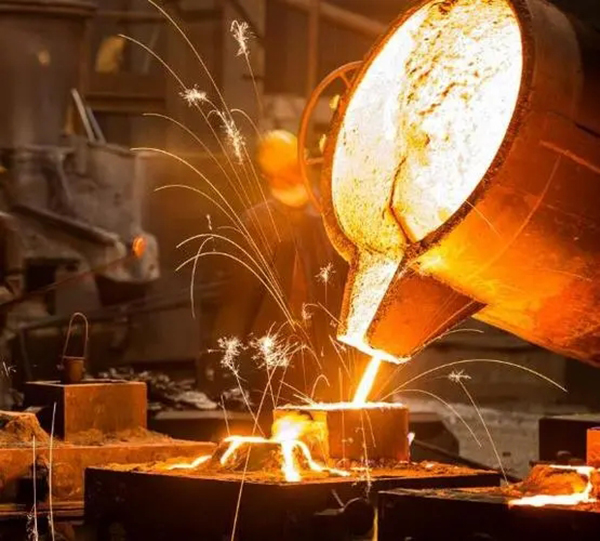

4.Forging
Forging is a processing method that uses forging machinery to exert pressure on metal ingredients to produce plastic deformation, improve strength and toughness, and obtain certain mechanical properties, certain shapes and sizes. Generally need machining to assist complete, suitable for the production of some large parts.
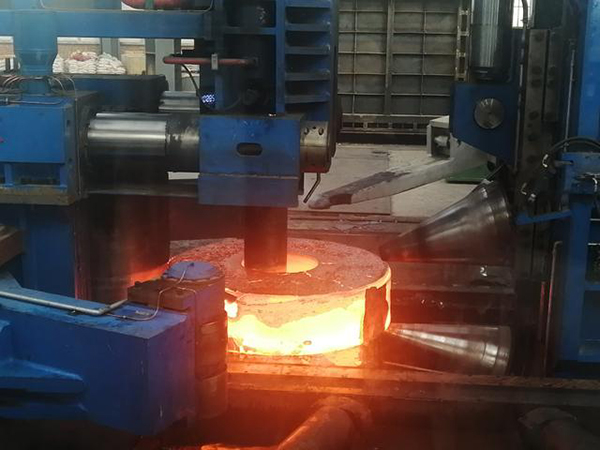

5.Welding
Welding is a processing method to connect two metal parts by heating or pressurizing, which is widely used in the manufacturing and repair of metal structures.

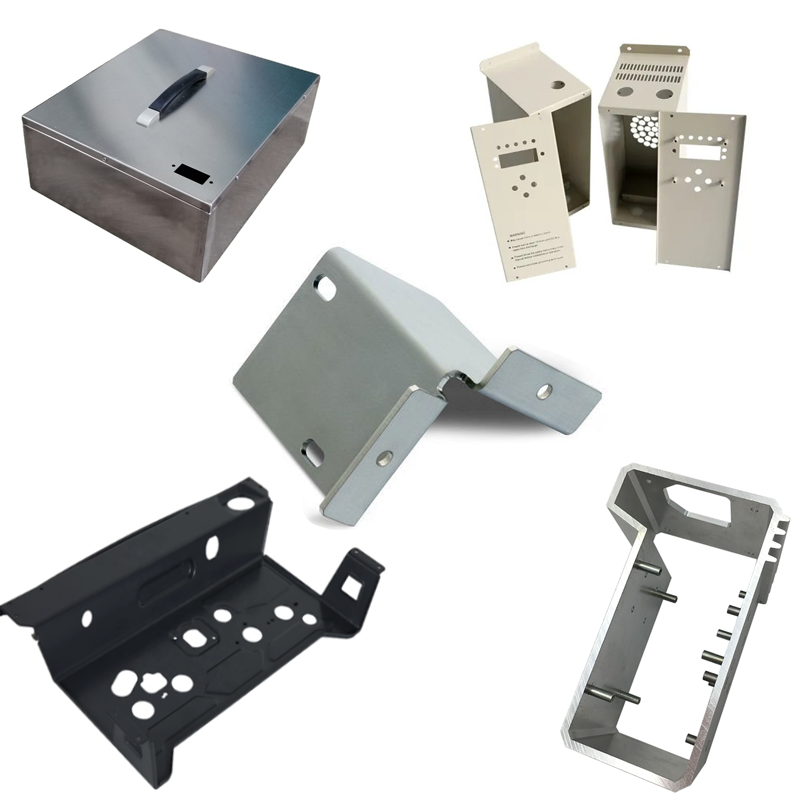
6.Cutting processing
By physically cutting a part of the material to achieve the required geometry and size, including turning, drilling, planing, milling and other ways. The desired geometry and size is achieved by physically cutting out a portion of the material. Suitable for any part processing.

These processes have their own characteristics, usually according to the specific needs of the product and design requirements to choose the appropriate processing method. In practical applications, multiple processes may be used in combination to achieve the best manufacturing results and economic benefits.